-
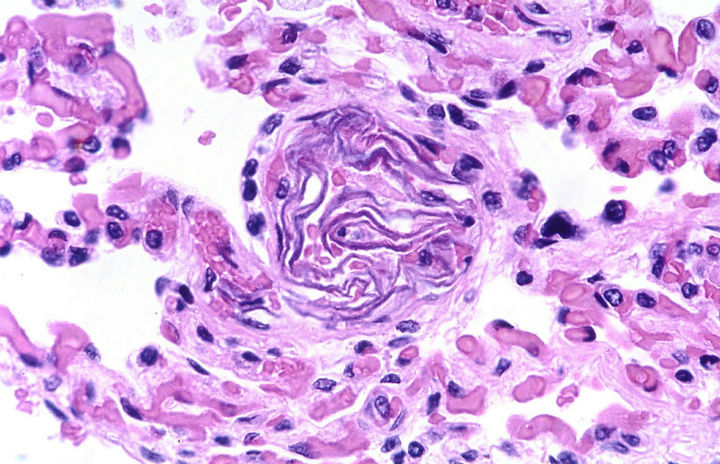
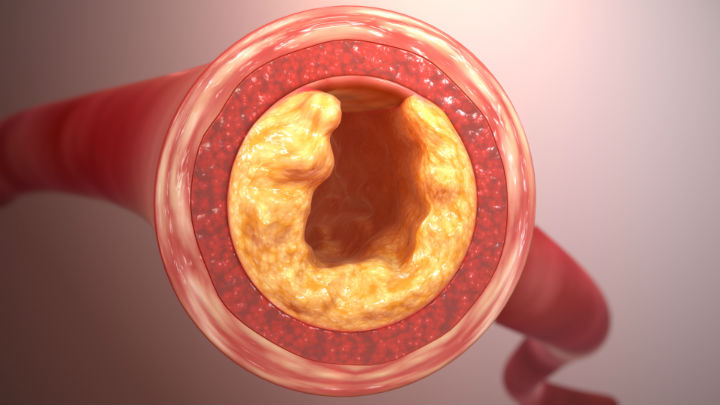
When something breaks loose into the bloodstream and travels around, it’s called an embolus. When the embolus comes to a place too small for it to pass through, it creates a blockage called an embolism. The cells on the other side can no longer receive blood flow and begin to...
-
An embolism occurs when an embolus, or moving particle within the blood vessels, gets stuck somewhere in the cardiovascular system. Blood can’t move past the embolus, and the cells on the other side become oxygen deprived, or “ischemic.” Embolisms can occur anywhere from the foot to the lungs to...
-
Pulmonary hypertension is a potentially life-threatening disease that affects the arteries connecting the heart to the lungs. These blood vessels narrow over time, which leads to an increase in blood pressure that causes additional damage and stress to them. While this damage cannot be reversed, with proper treatment, the...
-
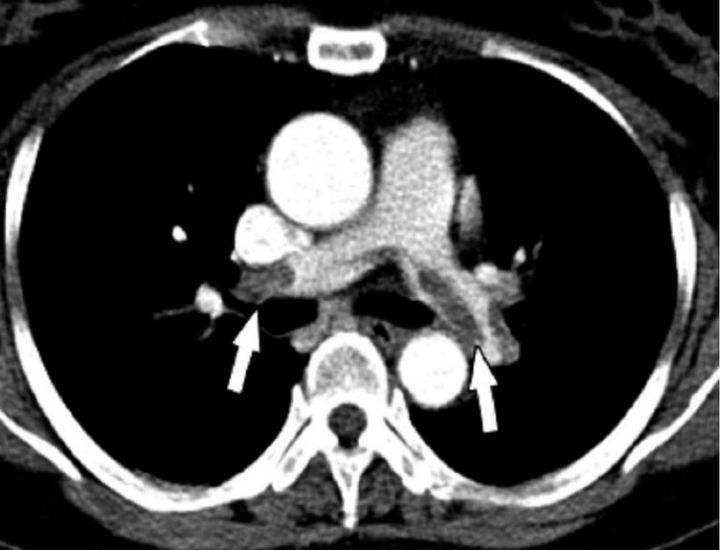
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage of a pulmonary artery, which is a blood vessel in the lung. Pulmonary arteries bring deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs, and this allows oxygen to be absorbed by the blood. Given the role of these arteries, pulmonary...
-
Pulmonary embolism is a serious, potentially life-threatening medical emergency in which a blood clot blocks an artery that brings blood to one or both lungs. Since blood flow to the lungs is the only way oxygen can enter the bloodstream, pulmonary embolism requires treatment as soon as possible. The...
-
An embolism occurs when a vein or artery is blocked by an embolus. Not to be confused with a thrombus (stationary blood clot), an embolus is a mobile substance confined to the blood vessels. There are several types of embolisms, depending upon the affected part of the body. The embolus...