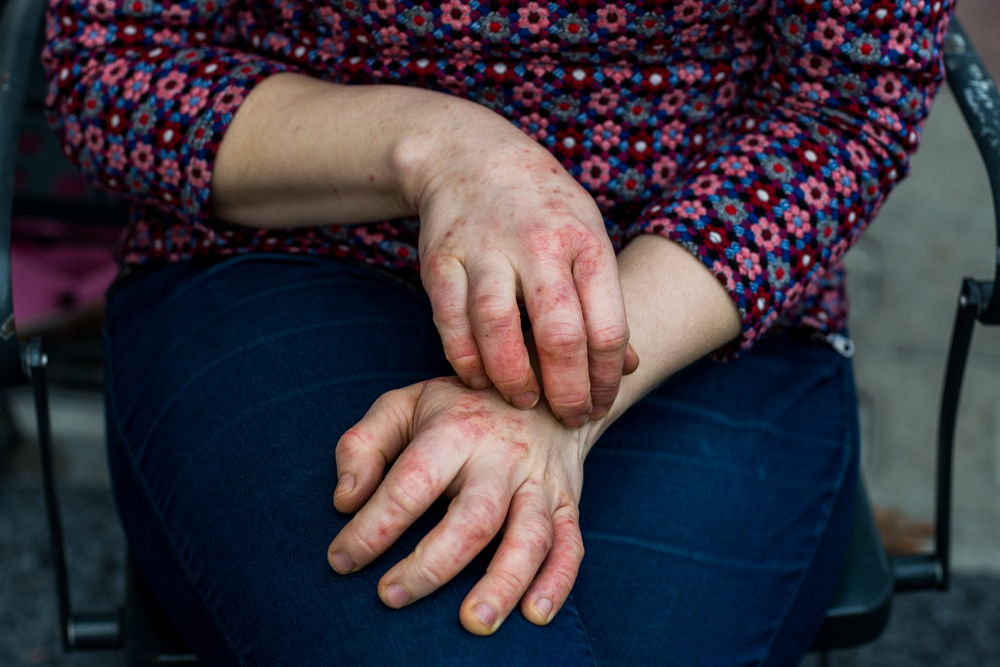
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that causes patches of red, dry, and itchy skin with periods of flare-ups and remissions. Typically concurrent with hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and asthma, Atopic dermatitis is incurable. However, there are numerous treatment options that can ease symptoms such as itching and keep flare-ups at bay.
Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
Every patient experiences varied atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms, but the most common symptoms associated with the condition are:
– Dry, rough, cracked, flaky, and itchy skin that may become inflamed and tender due to scratching
– Tiny, bumpy spots that may become pus-filled and get crusty upon scratching
– Red or brownish plaques forming on the neck, hands, wrists, chest, feet, ankles, in the folds of the knees and elbows
Atopic dermatitis typically begins to present itself before the age of 5 and continues into teens and adulthood. For some individuals, it is characterized by periods of outbreaks followed by times of remissions that can run for years.
Atopic Dermatitis Causes and Risk Factors
Skin that can function correctly is able to hold moisture to defend the body against allergens and irritants. Eczema is thought to have a connection to a genetic variation that disables this protective function of the skin, which makes the skin more susceptible to be impacted by environmental triggers such as allergens, bacteria, and irritants. Among children, even food allergies can play a part in the rise of atopic dermatitis.
A family history of atopic dermatitis, allergies, asthma, and allergic rhinitis (hay fever) increases one’s risk of developing atopic dermatitis.
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis does not call for any sort of lab test as your physician can reach a diagnosis by checking your medical records and performing a full examination of your skin. In some cases, your doctor may also opt to do patch testing or some additional tests to eliminate the possibility of other diseases that can cause similar symptoms or even figure out whether your atopic dermatitis is accompanied by another underlying condition.
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Treated?
Atopic dermatitis can be stubborn, requiring an attempt at a variety of treatment options over a long period to manage its symptoms. Even when a treatment approach is effective, this does not eliminate the possibility of recurring outbreaks. Early diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is vital to begin treatment as it may take a while before you have identified the most effective treatment options for your case.
If simply moisturizing on a regular basis and other home remedies do not improve your symptoms, your physician can recommend more potent treatment strategies that involve the use of corticosteroid ointments to relieve itching and restore the skin’s appearance. There are also some medications that can be used to manage inflammation as well as those that are used in case your skin gets infected.
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© oscity