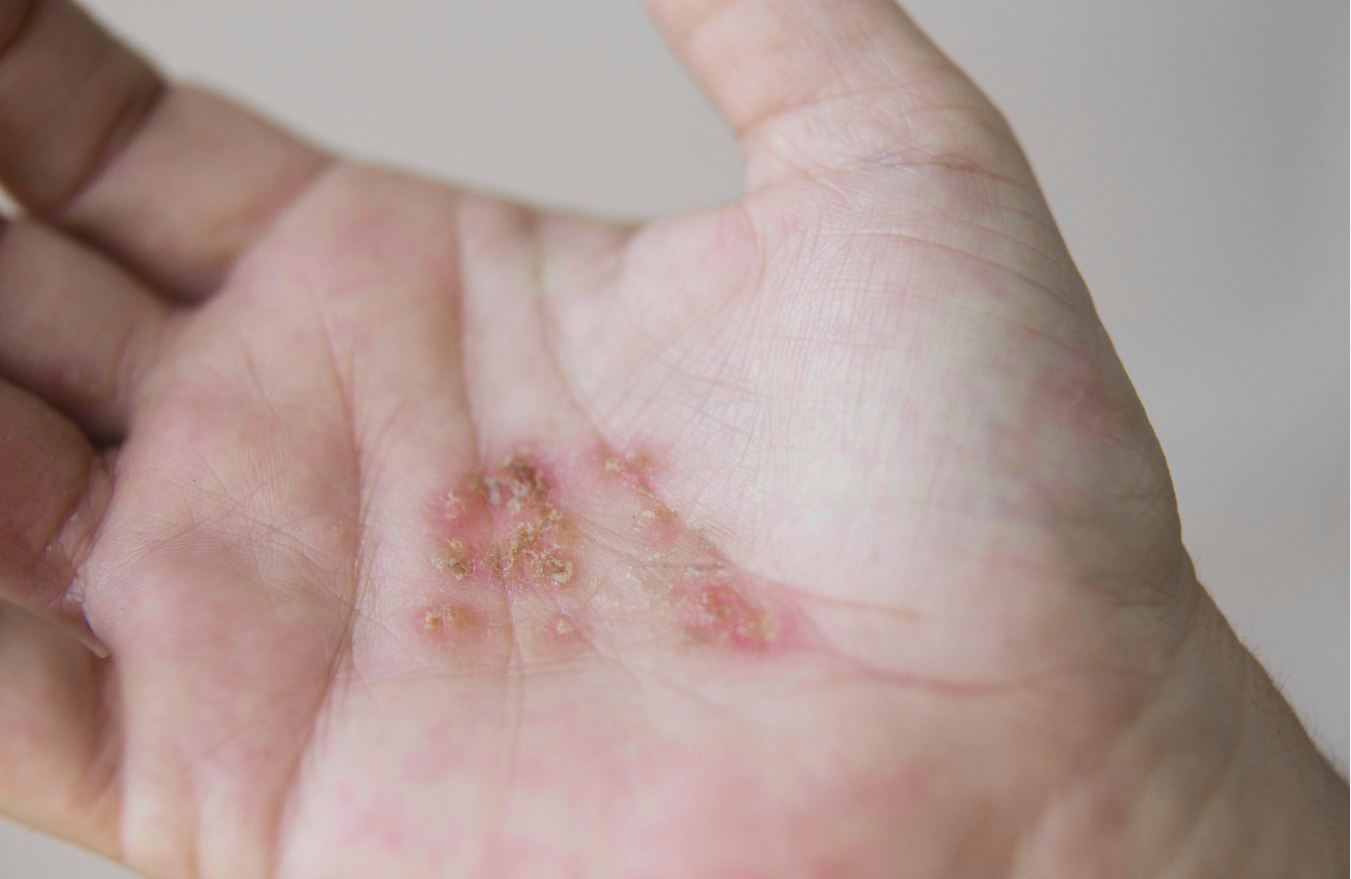
If you break out in red, flaky, and itchy rashes on your scalp, you may have seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis is a prevalent skin condition that resembles eczema (atopic dermatitis), psoriasis, or even a run-of-the-mill allergic reaction. Seborrheic dermatitis affects not only the scalp but can only target any oil-secreting part of the body such as the face or chest.
While medical experts have yet to identify the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis, they believe that a host of factors play a role in its development, including a gene variation, a fungus naturally present on the skin, and cold, dry climates.
People with oily complexions are more prone to developing seborrheic dermatitis. There are also some conditions that increase the risk of seborrheic dermatitis such as acne, depression, eating disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and psoriasis.
Treatment Options for Seborrheic Dermatitis
In some cases, seborrheic dermatitis can improve on its own without any need for treatment. However, in many cases, it is a chronic condition characterized by periods of outbreaks and remissions.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis may persist for years on end, but certain self-care strategies usually combined with medical treatment approaches can be effective in keeping the condition under control.
Adults who experience seborrheic dermatitis symptoms on their scalp (also known as dandruff) can initially resort to the use of over-the-counter therapy options such as a dandruff shampoo containing ketoconazole, coal tar, salicylic acid, or zinc pyrithione.
It is important to keep the affected parts of your body and face as clean as possible using a mild soap for sensitive skin and water on a daily basis. Controlled amounts of sunlight exposure can be beneficial in impeding the production of the yeasts that are responsible for inflammation, which is why spending enough time outside and exercising regularly outdoors can go a long way in improving your rashes. Of course, make sure to always properly apply sunscreen.
If you find that over-the-counter treatment options and home treatment strategies do not prove effective, you can consult your doctor for more potent treatment options, which may include the use of antifungal medicines, corticosteroid ointments, prescription-strength medicinal shampoos, and products containing sulfur.
In most cases, the most effective mode of treatment involves combining a number of approaches while making some lifestyle changes. Avoid using a medication or starting a treatment without consulting your primary physician given that there may be adverse side effects to some treatments, particularly in the long run.
If your symptoms worsen with the affected areas becoming swollen, inflamed, and pus-filled, make an appointment to visit your doctor as soon as possible.
Featured Image: Twitter