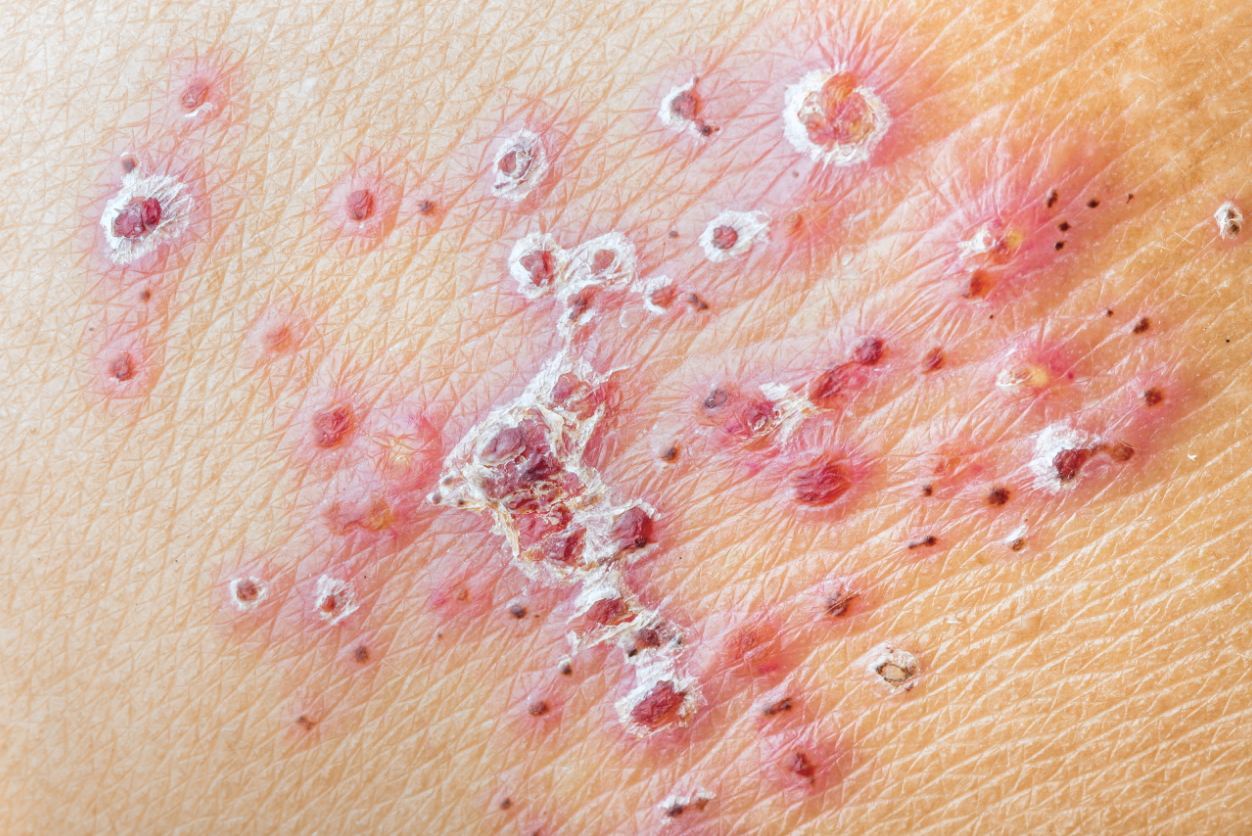
Herpes simplex is a viral disease caused by herpes simplex virus. Infections are classified according to the part of the infection.Oral herpes includes the face and mouth.It can cause small blisters, often called cold sores or fever blisters, or just sore throats. Herpes vulva, commonly referred to as herpes simplex, may have mild symptoms or form blisters that rupture, leading to small ulcers. These usually heal after two to four weeks.Before the blister, there may be tingling or shooting pain. Herpes simplex circulates between active and asymptomatic periods. The first attack is usually more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pain, enlarged lymph nodes, and headache. Over time, the frequency and severity of active disease attacks decreases.Other diseases caused by herpes simplex include: when it comes to finger herpetic white lotus, eyes type of herpes, herpes infection of the brain, when the impact to the newborn and neonatal herpes, etc.
Herpes simplex virus has two types, type 1 (hsv-1) and type 2 (hsv-2).hsv-1 is more likely to cause oral infection, while hsv-2 is more likely to cause genital infection. They are transmitted through direct contact with bodily fluids or the lesions of infected individuals.When symptoms do not exist, can still be transmitted.genital herpes are classified as sexually transmitted infections. It can spread to babies during childbirth. After infection, the virus travels along sensory nerves to nerve cell bodies, where it lives for life. The causes of recurrence may include: decreased immune function, stress and sunlight exposure.According to the appearance of symptoms, it is usually diagnosed as herpes simplex of the mouth and genitals. The diagnosis can be confirmed by virus culture or by detecting herpes DNA in fluids from blisters. Blood tests for antibodies to the virus can confirm previous infections, but are negative in new infections.
HSV infection can cause several different medical diseases. Common skin or mucosal infections can affect the face and mouth (herpes simplex in the face of the mouth), genital (genital herpes), or hand (herpes simplex bellow).More serious diseases occur when a virus infects and damages the eyes (herpes simplex keratitis) or invades the central nervous system, damaging the brain (herpes encephalitis).People who are immature or whose immune system is suppressed, such as newborns, transplant recipients or AIDS patients, are prone to severe complications of HSV infection.HSV infection is also associated with bipolar disorder, and cognitive impairment in alzheimer’s disease, although this is usually due to the patient’s genes.
As with almost all sexually transmitted infections, women are more susceptible to genital hsv-2 than men.Without the use of antiviral drugs or condoms, the risk of transmission of hsv-2 from infected men to women is about 8-11%.this is believed to be due to increased mucosal tissue exposure to potentially infected sites. The risk of transmission in infected women is about 4-5% per year. Inhibiting antiviral treatment can reduce the risk by 50%. Antiviral drugs also help prevent the development of symptomatic HSV in the presence of infection, which means that the infected partner is serologically positive but asymptomatic about 50% of the time.The use of condoms also greatly reduces the risk of transmission. Condom use is more effective in preventing transmission from men to women than vice versa. Previous hsv-1 infections may reduce the risk of hsv-2 infection in women by three times, although one study found that 14 out of 214 couples had a small sample of hsv-2 transmission.