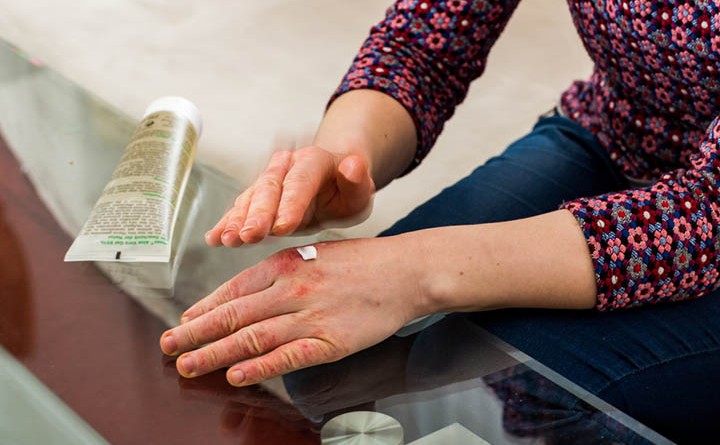
Eczema is an umbrella term for a group of skin conditions that cause patches of irritated, dry, and itchy skin. Atopic dermatitis is known as the most common prevalent form of eczema which is a term used interchangeably with eczema. Atopic dermatitis typically sets in during infancy and may persist into adulthood. That said, some individuals may get atopic dermatitis later in life.
Even though the exact cause of eczema remains mostly unknown, studies point to a variety of factors pertaining to genetics and environmental triggers. Simply put, eczema is brought on by an over-reactive immune system response. When an outside source prompts this immune system response, this results in frequent flare-ups. Individuals who have a family history of atopic dermatitis or other forms of eczema are also much more susceptible to develop eczema themselves. If you suffer from a type of eczema, you are in the same boat as over 30 million individuals in the United States.
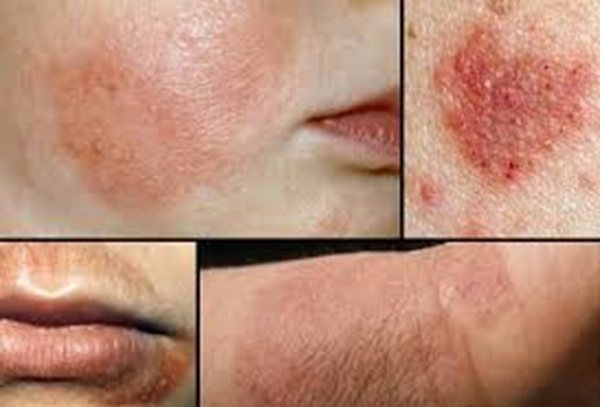
Atopic Eczema (Chronic Eczema)
Atopic dermatitis has a genetic basis. It is a chronic form of eczema. ‘Atopic’ means the condition is caused by allergy sensitivity. This particular condition tends to develop early in life, and as children who have atopic dermatitis grow older, this problem may get better or go away. Characteristically, rashes appear on the cheeks, neck, elbow and knee creases, and ankles. The treatment process focuses on healing damaged skin and alleviating symptoms. Mentioned below are a few of the many treatment processes.
Relief Methods
NSAID Ointment
There is a new prescription-strength ointment called Crisaborole that works as an anti-inflammatory. It is steroid-free and must be used twice daily. Patients 2 years and above can use this ointment. It brings the skin back to its normal appearance and reduces inflammation.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is commonly used in the treatment of severe eczema during which the skin is exposed to ultraviolet light. Patients must visit the doctor 2-3 times a week for up to 2-3 months. Phototherapy has the potential to improve the condition of over 70% of patients. The most commonly used ultraviolet light is ultraviolet B.
At-Home Skincare
Skincare involves a regimen that focuses on keeping your skin well-moisturized. An important measure is to avoid putting on clothing items made of rough, irritating material by choosing clothes with soft fabrics, preferably cotton. Take lukewarm baths and apply moisturizer to your skin right after every bath as this helps the skin barrier retain moisture. Avoid scratching the affected areas of your skin and keep your nails short. Using antihistamines may be an effective way to relieve itching.
Avoid contact with irritants such as wool and lanolin (an oily substance derived from sheep wool used in some moisturizers and cosmetics). Invest in a humidifier and run it in your bedroom when you feel too dry, and avoid using harsh soaps.
Wet Wrap Therapy
Wet wrap therapy is a traditional and highly effective treatment which involves the procedure of taking 3 lukewarm baths a day. Topical medicines and a moisturizer are then applied to the affected areas within 2-3 minutes and sealed using a wet cloth. If you are unsure as to how you can best apply wet dressings, consult with your doctor or a nurse for expert tips.
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© oscity




