Depression is not just a once-in-awhile, temporary bad mood — it is a constant feeling of worthlessness, unhappiness and complete disinterest in the desire to engage in regular, pleasurable life activities. Ordinarily, depression is usually treated with drugs, talk therapy or both. Sometimes drugs and talk therapy fail, forcing one to look for other alternatives. This then begs the question, can electronic therapies help with your depression?
Even with the ongoing research in the medical field, a lot of investment has been put in place to enhance non-medical solutions to handle depression. Not all the electronic therapies are widely available but this is an area that is promising.
Here are some of the well recognised electronic therapies:
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
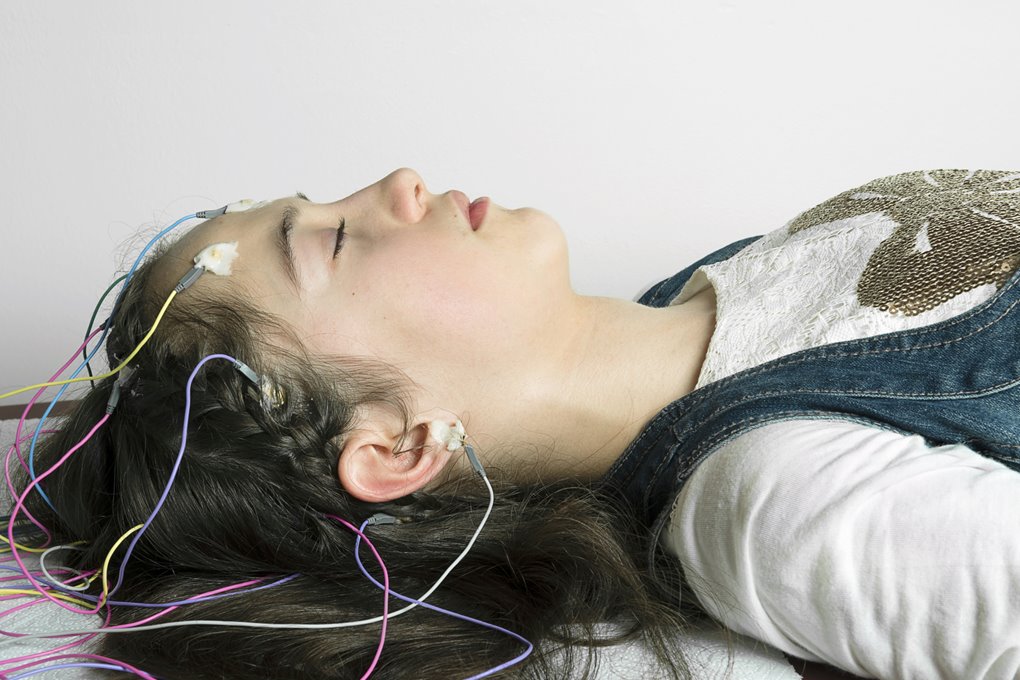
This therapy has been used for a period of time as an alternative treatment when all other methods have failed to help a depressed patient. This involves inducing seizure to the patient through a current that is passed through electrodes that are attached to the patient’s scalp. This treatment is usually administered under normal anesthesia two or three times every week for three or four weeks.
ECT has some side effects which include: vomiting, nausea, headache and jaw pain on the day the treatment is administered. Long term side effects include confusion that may last up to a few hours, loss of memory which sometimes can last for a few months.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
For this type of treatment, a device has to be attached in the vagus nerve and implanted in the patient’s chest. This is usually achieved through surgery. The device is then activated to stimulate the vagus nerve thirty seconds in every five minutes. The effects of this device include changes in the brain metabolism especially in the regions of the brain where dopamine is produced.
These changes can be monitored through Pet scans. The overall outcome is a feeling of relief for several months. The majority of patients who have used this method have shown remarkable improvement and considerable reduction of depressive symptoms in the long run. This method of therapy is rarely used because of the risks that come with one being involved in surgery.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
This method makes use of magnetic waves which are passed through the parts of the brain that are responsible for regulation of a person’s mood. This is achieved by placing a powerful magnet over a region of the brain called the prefrontal cortex for short intervals of time. This is a daily treatment involving sessions that may take several weeks. This treatment was approved in 2008 by the FDA . The benefits of this treatment are long lasting with very few side effects. However not all patients usually respond to this type of treatment
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES)
This type of treatment uses low intensity pulsed current that is applied to the scalp or ear lobes. It has no side effects apart from rare mild pains on the scalp or skin areas. This treatment is approved by FDA for the treatment of nervousness sleeplessness, and depression. The CES devices are available for therapy in a number of companies for personal use.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
This type of therapy is experimental and serves different purposes. It uses two electrodes that are placed over a persons head and direct light electrical current passed through them. The anode electrode is responsible for stimulation of neuronal action while the cathode electrode is responsible for reduction of the neuronal action. This treatment has no known side effects. It has been used to treat chronic pain, depression, anxiety and Parkinson’s disease
Image source: Thinkstock/minemero