Eczema is a common skin condition that results in the appearance of red, inflamed, dry, and itchy patches of skin. The reaction is typically marked by red, bumpy plaques with fluid-filled blisters. When the blisters break open, the affected skin can ooze pus. In chronic eczema, the blisters are less noticeable but the skin gets hardened, rough, and scaly. There are numerous types of skin conditions that resemble eczema, so a correct diagnosis is important in addressing a patient’s complaints.
A proper skincare regimen that includes moisturizing regularly is essential in the prevention of various types of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. Unfortunately, eczema is not a condition that can be cured; it can only be treated to improve symptoms. The treatment process usually aims to repair cracked, damaged skin and lessening the severity of overall symptoms.
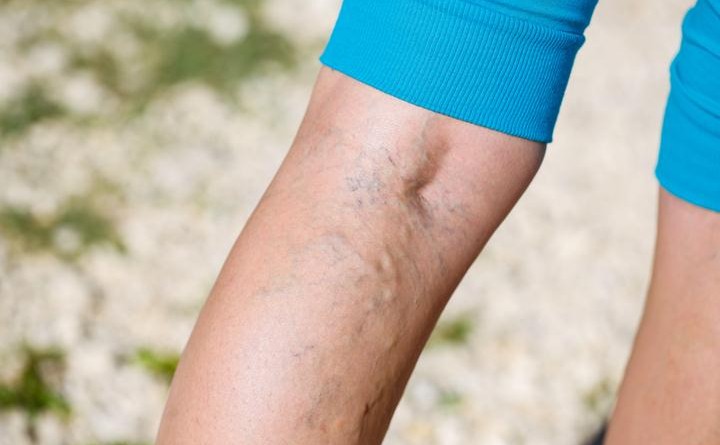
Varicose Eczema
The reaction pattern consists of a red elevated plaque with red fluid-filled blisters. The skin looks red and can be slightly shiny. Varicose Eczema more commonly affects older people. As many as one in five people over the age of 70 develop varicose eczema. It affects people with varicose veins or have had a varicose vein surgery. Those who have had a thrombosis in a deep leg vein too may suffer from this disease.
Treatment
Compression Socks
Compression stockings need to be worn in the morning and taken off when it is time for bed. They are specially designed stockings that squeeze the legs tightly at the foot and ankle and become looser further up the leg. This helps improve circulation.
Emollients
Emollients are key in the management of varicose eczema. It is a moisturizer applied to the skin. Apply within 30 minutes of taking a bath to lock in the moisture. It must be applied in large amounts. In case of extremely dry skin, apply the emollient every 2-3 hours to keep the impact of the moisturizer intact.
NSAID Ointment
There is a new prescription-strength anti-inflammatory called Crisaborole on the market. It is non-steroidal and must be applied to affected areas twice a day. Patients 2 years and above can use this ointment. It brings the skin back to its normal appearance and reduces inflammation.
Skincare at Home
Skin care involves a process of keeping the skin well-moisturized. Avoid wearing clothes with rough or prickly material and opt for clothing items with soft fabric that is made of 100% cotton. Take warm baths daily and follow it up with a thorough application of a moisturizer of your choice that helps with dryness. Resist to urge to scratch the affected parts of your skin and keep your nails short. Consult with your doctor about the use of antihistamines to ease intense itching.
Keep away from irritants such as wool and lanolin (an oily substance derived from sheep wool used in some moisturizers and cosmetics). Keep a humidifier in the room as well. Finally, use mild soaps while bathing.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical Corticosteroids are ointments and creams applied to the skin to help treat varicose eczema. Apply an emollient first and wait around 30 minutes before applying the prescribed topical corticosteroid. Do not apply in large amounts and dab the ointment only on the affected areas.
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© zlikovec